Home > D. General pathology > lymphomatoid granulomatosis
lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Thursday 12 August 2004
angiocentric immunoproliferative lesion, AIL, angiocentric lymphoproliferative lesion, benign lymphocytic angiitis and granulomatosis
Digital cases
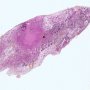
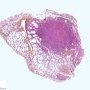
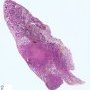
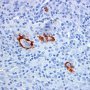
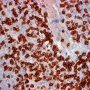
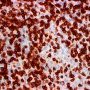
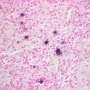
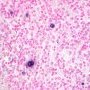
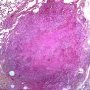
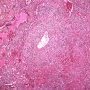
JRC:1608 : Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis.
JRC:19434 : Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis.
Definition: Lymphomatoid granulomatosis is a rare lesional syndrome associated with Epstein-Barr virus EBV-associated B-cell LPD or peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis is an angio-destructive lymphoproliferative disorder (LPD) with prominent pulmonary involvement.
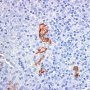
Most LYG are an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated B-cell LPD with large numbers of background reactive T lymphocytes (T cell-rich B cell lymphoma) and can be considered as a rare angiocentric and angiodestructive form of EBV-associated B-cell LPD.
Some are associated with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (7573693, 11085664).
Synopsis
angiocentric immunoproliferative lesion
- angiocentric or angiodestructive lesions with lymphocytic infiltrates (angioinvasion)
- marked angiocentric lymphohistiocytic infiltrate, composed predominantly of CD4-positive T-cells, with angiodestruction and necrosis
zonal necrosis
atypical tumoral cells
- associated EBV-associated peripheral B-cell lymphoma
- associated peripheral T-cell lymphoma (11085664)
Localization
pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis
cerebral lymphomatoid granulomatosis (20%)
cutaneous lymphomatoid granulomatosis (11688570)
digestive lymphomatoid granulomatosis
renal lymphomatoid granulomatosis
hepatic lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Predisposition
secondary immunodeficiencies
- HIV infection and AIDS (11296596, 2703227)
- chemotherapy (11331732, 12571471)
- autologous stem cell transplantation
- immunosuppression
-
- immunosuppression for dysimmune disease
- immunosuppression for Crohn disease
- immunosuppression for dysimmune disease
primary immunodeficiencies
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)
- common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) (12803130)
Associations
Wegener granulomatosis (12136927)
References
Guinee DG Jr, Perkins SL, Travis WD, Holden JA, Tripp SR, Koss MN. Proliferation and cellular phenotype in lymphomatoid granulomatosis: implications of a higher proliferation index in B cells. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998 Sep;22(9):1093-100. PMID: 9737242
Guinee D Jr, Jaffe E, Kingma D, Fishback N, Wallberg K, Krishnan J, Frizzera G, Travis W, Koss M. Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Evidence for a proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus infected B-lymphocytes with a prominent T-cell component and vasculitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994 Aug;18(8):753-64. PMID: 8037289
Myers JL, Kurtin PJ, Katzenstein AL, Tazelaar HD, Colby TV, Strickler JG, Lloyd RV, Isaacson PG. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Evidence of immunophenotypic diversity and relationship to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Nov;19(11):1300-12. PMID: 7573693