Home > E. Pathology by systems > Respiratory system > Lungs > pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis
pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Tuesday 16 November 2004
Digital case
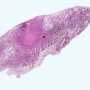
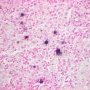
JRC:1608 : Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis.
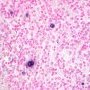
JRC:19434 : Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis.
Definition: Lymphomatoid granulomatosis is a rare lesional syndrome associated with Epstein-Barr virus EBV-associated B-cell LPD. It is an angio-destructive lymphoproliferative disorder (LPD) with prominent pulmonary involvement.
Most LYG are an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated B-cell LPD with large numbers of background reactive T lymphocytes (T cell-rich B cell lymphoma) and can be considered as a rare angiocentric and angiodestructive form of EBV-associated B-cell LPD. However, some are associated with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (7573693, 11085664).
Synopsis
angiocentric immunoproliferative lesion
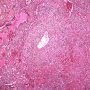
- angiocentric or angiodestructive lesions with lymphocytic infiltrates (angioinvasion)
- marked angiocentric lymphohistiocytic infiltrate, composed predominantly of CD4-positive T-cells, with angiodestruction and necrosis
zonal necrosis
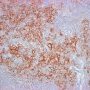
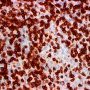
tumor nodules: mixture of atypical large CD20+ lymphocytes, with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli and with a background of small and intermediate-size T-lymphocytes, histiocytes, and plasma cells.
EBV1-encoded RNA present in CD20+ large, atypical lymphocytes
Predisposition
secondary immunodeficiencies
- HIV infection (11296596)
- chemotherapy (11331732, 12571471)
- autologous stem cell transplantation
- organ allograft (12802639)
primary immunodeficiencies
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)
- common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
Subtypes
grade 1 lymphomatoid granulomatosis
grade 2 lymphomatoid granulomatosis
grade 3 lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Differential diagnosis
Wegener granulomatosis
varicella-zoster-related pneumonia
bronchocentric granulomatosis
Hodgkin lymphoma
peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCLs)
natural killer cell lymphoma (NKCL)
Other localization
pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis
cerebral lymphomatoid granulomatosis (20%)
cutaneous lymphomatoid granulomatosis (11688570)
digestive lymphomatoid granulomatosis
renal lymphomatoid granulomatosis
hepatic lymphomatoid granulomatosis
References
Guinee DG Jr, Perkins SL, Travis WD, Holden JA, Tripp SR, Koss MN. Proliferation and cellular phenotype in lymphomatoid granulomatosis: implications of a higher proliferation index in B cells. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998 Sep;22(9):1093-100. PMID: 9737242
Guinee D Jr, Jaffe E, Kingma D, Fishback N, Wallberg K, Krishnan J, Frizzera G, Travis W, Koss M. Pulmonary lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Evidence for a proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus infected B-lymphocytes with a prominent T-cell component and vasculitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994 Aug;18(8):753-64. PMID: 8037289
Myers JL, Kurtin PJ, Katzenstein AL, Tazelaar HD, Colby TV, Strickler JG, Lloyd RV, Isaacson PG. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Evidence of immunophenotypic diversity and relationship to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Nov;19(11):1300-12. PMID: 7573693