Home > D. Systemic pathology > Genetic and developmental anomalies > Pfeiffer syndrome
Pfeiffer syndrome
MIM.101600
Wednesday 1 December 2004
Autosomal dominant disease
Synopsis
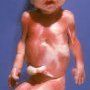
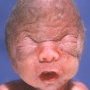
![]() craniofacial anomalies
craniofacial anomalies
- craniosynostosis
- turribrachycephaly
- occasional clover-leaf skull
- maxillary hypoplasia
- mandibular prognathism
- shallow orbits
- hypertelorism
- down-slanting palpebral fissures
- proptosis
- strabismus
- small nose with low nasal bridge
- choanal atresia or stenosis
- high arched palate
- dental crowding
![]() chondromalacia
chondromalacia
- laryngomalacia
- tracheomalacia
- bronchomalacia
- coronal craniosynostosis with or without
- +/- sagittal craniosynostosis
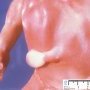
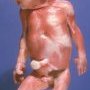
![]() limbs anomalies
limbs anomalies
- dadiohumeral synostosis of elbow
- broad thumb and broad great toe
- partial syndactyly of fingers and toes
- brachymesophalangy of hands and feet
![]() cerebral anomalies
cerebral anomalies
Subtypes
![]() Type 1: ’mild’ autosomal dominant
Type 1: ’mild’ autosomal dominant ![]() Type 2: cloverleaf skull, elbow ankylosis, early demise, sporadic
Type 2: cloverleaf skull, elbow ankylosis, early demise, sporadic ![]() Type 3: craniosynostosis, early demise, sporadic (Cohen, 1993).
Type 3: craniosynostosis, early demise, sporadic (Cohen, 1993).
Etiology
![]() Locus 8p11.2-p11.1: germline mutations in the gene FGFR1 coding for fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (MIM.136350)
Locus 8p11.2-p11.1: germline mutations in the gene FGFR1 coding for fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (MIM.136350)
![]() Locus 10q26: germline mutations in the gene FGFR2 coding for fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 (MIM.176943)
Locus 10q26: germline mutations in the gene FGFR2 coding for fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 (MIM.176943)
See also:
![]() craniosynostosis
craniosynostosis![]() FGFRs
FGFRs