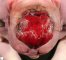
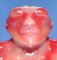
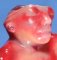
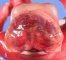
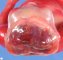
Definition: Anencephaly is a designation for congenital absence of the cranial vault with cerebral hemispheres completely missing or decreased to small masses attached to the base of the skull. In anencephaly, the absence of the brain and calvaria can be total or partial. Anencephaly is one of the neural tube defects (NTDs).
The etiology is unknown. Whether the bony tissue or soft brain tissue is a primary factor is also unknown.
Synopsis
![]() congenital absence of the cranial vault
congenital absence of the cranial vault
![]() cerebral hemispheres completely missing or decreased to small masses attached to the base of the skull
cerebral hemispheres completely missing or decreased to small masses attached to the base of the skull
![]() The absence of the brain can be total or partial.
The absence of the brain can be total or partial.
![]() The absence of thecalvaria can be total (acrania) or partial.
The absence of thecalvaria can be total (acrania) or partial.
![]() bactracian facial dysmorphism
bactracian facial dysmorphism
![]() absent frontal bones
absent frontal bones
![]() shallow orbits
shallow orbits
![]() protusion of the eyeballs
protusion of the eyeballs
Types
![]() isolated anencephaly
isolated anencephaly
- sporadic anencephaly
- familial anencephaly
![]() syndromal anencephaly
syndromal anencephaly
- associated anencephaly (see Associations)
![]() holoacrania form of anencephaly
holoacrania form of anencephaly
Associations
![]() bilateral adrenal hypoplasia
bilateral adrenal hypoplasia
![]() cardiac malformations
cardiac malformations
- aortic coarctation
- left heart hypoplasia (left ventricular hypoplasia)
![]() cleft lip/palate
cleft lip/palate
![]() spina bifida
spina bifida
![]() complete rachischisis
complete rachischisis
![]() short-rib polydactyly syndrome (SRPS) (8267012)
short-rib polydactyly syndrome (SRPS) (8267012)
![]() congenital diaphragmatic hernia
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
![]() macrosomia
macrosomia
![]() cystic renal dysplasia
cystic renal dysplasia
Etiology
![]() sporadic
sporadic
![]() familial anencephaly (2333913)
familial anencephaly (2333913)
- parental consanguinity (2333913)
NB: Posterior fossa
A study showed 2 morphologic types of the posterior cranial fossa. One type had a fossa cranial morphology close to normal morphology, whereas the other had a malformed and much smaller posterior cranial fossa. The latter condition was presumed to be due to a primary error in chondral and cranial development. (15630528)
See also
![]() cerebral malformations
cerebral malformations
![]() neural tube defects (NTDs)
neural tube defects (NTDs)
Animal models
![]() mice that are homozygous for deficiency in the paired class homeobox-containing gene Cart1
mice that are homozygous for deficiency in the paired class homeobox-containing gene Cart1
References
![]() Lomholt JF, Fischer-Hansen B, Keeling JW, Reintoft I, Kjaer I. Subclassification of anencephalic human fetuses according to morphology of the posterior cranial fossa. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2004 Nov-Dec;7(6):601-6. Epub 2004 Nov 17. PMID: 15630528
Lomholt JF, Fischer-Hansen B, Keeling JW, Reintoft I, Kjaer I. Subclassification of anencephalic human fetuses according to morphology of the posterior cranial fossa. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2004 Nov-Dec;7(6):601-6. Epub 2004 Nov 17. PMID: 15630528