Home > A. Molecular pathology > TSC1
TSC1
9q34
Friday 23 April 2004
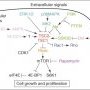
The TSC1-TSC2 complex functions as GTPase activating protein against Rheb - a Ras-like small GTPase, which in turn regulates TOR signaling in nutrient-stimulated cell growth.
TSC1 and TSC2 receive input from several signalling pathways, including the PI3K-Akt (insulin-signalling) pathway, the ERK1/2 pathway, the p38MAPK-MK2 pathway and the LKB1-AMPK (energy-sensing) pathway, as well as GSK3β. Also, there is probably direct input from signalling in response to hypoxia.
In response to these signals, TSC1-2 acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for Rheb, which, in turn, regulates mTOR. Activated mTOR has two main downstream targets, S6K and 4E-BP1. This process activates cell growth and proliferation.
Pathology
germline mutations in tuberous sclerosis
somatic mutations in tumors
- in vesical urothelial carcinoma (12%)
See also
FRAP1 (mTOR)
tuberous sclerosis
Locus TSC2 (MIM.191092) at 16p13.3
Locus TSC3 at 12q14 (MIM.191091)
Locus TSC4 (MIM.191090)
References
Findlay GM, Harrington LS, Lamb RF. TSC1-2 tumour suppressor and regulation of mTOR signalling: linking cell growth and proliferation? Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005 Feb;15(1):69-76. PMID: 15661536
Inoki K, Corradetti MN, Guan KL. Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway in human disease. Nat Genet. 2005 Jan;37(1):19-24. PMID: 15624019
Fingar DC, Blenis J. Target of rapamycin (TOR): an integrator of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 2004 Apr 19;23(18):3151-71. PMID: 15094765
Pan D, Dong J, Zhang Y, Gao X. Tuberous sclerosis complex: from Drosophila to human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;14(2):78-85. PMID: 15102439
Yeung RS. Multiple roles of the tuberous sclerosis complex genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2003 Dec;38(4):368-75. PMID: 14566857