Home > E. Pathology by systems > Digestive system > Liver and pancreatobiliary system > Pancreas > intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
Thursday 16 October 2008
pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous tumors; intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas; IPMNs; IPMN
| PO |
Definition: Intraductal grossly visible (1 cm or more) epithelial neoplasm of mucin producing cells, arising in main pancreatic duct or its branches.
Images
Macroscopy : IPMN
- https://twitter.com/GeronimoJrLapac/status/856424085441699840
- https://twitter.com/BeynonMD/status/833411358821597188
- https://twitter.com/PancPathologist/status/836582726014799874
Neoplastic epithelium is usually papillary; variable mucin secretion, duct dilatation (cyst formation), and dysplasia; classify based on highest degree of cytoarchitectural atypia and invasiveness as:
IPMN with low- to intermediate-grade dysplasia; previously called intraductal papillary mucinous adenoma
IPMN with high grade dysplasia; previously called intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma, non invasive
IPMN with associated invasive carcinoma (WHO)
It is one of three precursor lesions of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (also PanIN, Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm).
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) are an increasingly recognized precursor to invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas.
Images
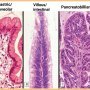
4 subtypes
FNA cytology : IPMN vs MCN +/-atypia
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in MMR deficiency
Subtypes
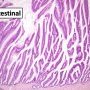
intestinal IPMN
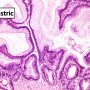
gastric IPMN
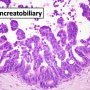
pancreatobiliary IPMN
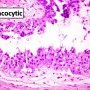
oncocytic IPMN
Cytogenetics
polysomy 6 and p16 deletion may contribute to adenomatous change of IPMN; (25517961)
polysomy 7, polysomy 18, p16 deletion, and p53 deletion play roles in malignant transformation of non-invasive IPMN; (25517961)
polysomy 7 and p53 deletion may be excellent diagnostic markers for invasive IPMN. (25517961)
See also
PanIN / PanINs : pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia
pancreatic cystic anomalies
Open References
Locus/Chromosome Aberrations in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Analyzed by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization. Miyabe K, Hori Y, Nakazawa T, Hayashi K, Naitoh I, Shimizu S, Kondo H, Nishi Y, Yoshida M, Umemura S, Kato A, Ohara H, Joh T, Inagaki H. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014 Dec 16. PMID: 25517961 (Free)
In vivo and in vitro propagation of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
Kamiyama H, Kamiyama M, Hong SM, Karikari CA, Lin MT, Borges MW, Griffith M, Young A, Norris-Kirby A, Lubek C, Mizuma M, Feldmann G, Shi C, Liang H, Goggins MG, Maitra A, Hruban RH, Eshleman JR. Lab Invest. 2010 May;90(5):665-73. doi : 10.1038/labinvest.2010.51. Epub 2010 Mar 15 PMID: 20231822 Free
References
A Revised Classification System and Recommendations From the Baltimore Consensus Meeting for Neoplastic Precursor Lesions in the Pancreas.
Basturk O, Hong SM, Wood LD, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Biankin AV, Brosens LA, Fukushima N, Goggins M, Hruban RH, Kato Y, Klimstra DS, Klöppel G, Krasinskas A, Longnecker DS, Matthaei H, Offerhaus GJ, Shimizu M, Takaori K, Terris B, Yachida S, Esposito I, Furukawa T; Baltimore Consensus Meeting.
Am J Surg Pathol. 2015 Dec;39(12):1730-41.
doi : 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000533
PMID: 26559377
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Shi C, Hruban RH. Hum Pathol. 2012 Jan;43(1):1-16. doi : 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.04.003
PMID: 21777948
Hong SM, Kelly D, Griffith M, Omura N, Li A, Li CP, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Multiple genes are hypermethylated in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Mod Pathol. 2008 Sep 26. PMID: 18820670