congenital lobar hyperinflation
Image Gallery
[ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Congenital lobar emphysema}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Congenital lobar emphysema}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Congenital lobar emphysema}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Congenital lobar hyperinflation}) ] [ (||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Congenital lobar hyperinflation}) ]Definition: Congenital lobar hyperinflation (or congenital lobar emphysema) is the most frequent fetal/neonatal pulmonary anomaly, before congenital pulmonary airway malformations (CPAMs).
Lobar hyperinflation in the neonate is usually congenital, resulting from cartilage deficiency causing bronchomalacia and distal air trapping.
Nota bene: An acquired lobar hyperinflation is usually associated with chronic lung disease or endobronchial obstruction such as mucus plugging or a pedunculated endobronchial polyp. (#17206431#)
Synopsis
![]() Resection of a hyperlucent left upper lobe
Resection of a hyperlucent left upper lobe
![]() roughly triangular overdistended area of lung
roughly triangular overdistended area of lung
![]() cut surface: few tiny apparent cysts beneath the pleura
cut surface: few tiny apparent cysts beneath the pleura
![]() overinflation of a lobe of lung
overinflation of a lobe of lung
![]() usually middle or upper lobe
usually middle or upper lobe
![]() Compression of surrounding normal lung
Compression of surrounding normal lung
![]() May demonstrate partial bronchial obstruction
May demonstrate partial bronchial obstruction
![]() Frequently no anatomic cause can be found
Frequently no anatomic cause can be found
![]() Presents with dyspnea in the first weeks of life
Presents with dyspnea in the first weeks of life
![]() Lucent area on chest x-ray
Lucent area on chest x-ray
![]() Surgically excised lobe is filled with air
Surgically excised lobe is filled with air
- does not collapse after removal
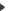 Microscopically shows distended air spaces
Microscopically shows distended air spaces - best appreciated by comparing with age-matched control lung
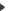 overdistension of alveoli and alveolar ducts (to four to five times the normal diameter).
overdistension of alveoli and alveolar ducts (to four to five times the normal diameter). - The magnitude of the distension may not be evident until compared with an age-matched control section of lung.
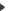 possible interstitial emphysema
possible interstitial emphysema
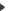 rare bronchial obstruction associated
rare bronchial obstruction associated
Differential diagnosis
![]() unilobar congenital pulmonary lymphangiectasis (#15136998#)
unilobar congenital pulmonary lymphangiectasis (#15136998#)
Associations
![]() intralobar pulmonary sequestration (#15995872#)
intralobar pulmonary sequestration (#15995872#)
![]() pulmonary lobar lymphangiectasis (HP.13341) (#4715376#, #5936105#)
pulmonary lobar lymphangiectasis (HP.13341) (#4715376#, #5936105#)
![]() lobar bronchial atresia (#7093137#, #17101340#, #5775061#)
lobar bronchial atresia (#7093137#, #17101340#, #5775061#)
![]() abnormal bronchial cartilage (#7093137#)
abnormal bronchial cartilage (#7093137#)
![]() polysplenia (#20864788#)
polysplenia (#20864788#)
![]() great vessel anomaly (left aortic arch, right descending aorta and left ligamentum arteriosum) (#18937763#)
great vessel anomaly (left aortic arch, right descending aorta and left ligamentum arteriosum) (#18937763#)
![]() laryngotracheal cleft (#17635408#)
laryngotracheal cleft (#17635408#)
![]() congenital heart disease (#16616669#)
congenital heart disease (#16616669#)
![]() lobus venae azygos (#2982179#)
lobus venae azygos (#2982179#)
![]() bronchial sling around a normal right main pulmonary artery (#875429#)
bronchial sling around a normal right main pulmonary artery (#875429#)
See also
![]() lungs
lungs
- pulmonary malformations
References
![]() Ball valve obstruction of a bronchus causing lobar emphysema in a neonate. Clubley E, England RJ, Cullinane C, Crabbe DC. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007 Jul;23(7):699-702. PMID: #17206431#
Ball valve obstruction of a bronchus causing lobar emphysema in a neonate. Clubley E, England RJ, Cullinane C, Crabbe DC. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007 Jul;23(7):699-702. PMID: #17206431#
![]() Mani H, Suarez E, Stocker JT. The morphologic spectrum of infantile lobar emphysema: a study of 33 cases. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004;5 Suppl A:S313-20. PMID: #14980289#
Mani H, Suarez E, Stocker JT. The morphologic spectrum of infantile lobar emphysema: a study of 33 cases. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004;5 Suppl A:S313-20. PMID: #14980289#
![]() Congenital lobar emphysema: a case with bronchial atresia and abnormal bronchial cartilages. Warner JO, Rubin S, Heard BE. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Apr;76(2):177-84. PMID: #7093137#
Congenital lobar emphysema: a case with bronchial atresia and abnormal bronchial cartilages. Warner JO, Rubin S, Heard BE. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Apr;76(2):177-84. PMID: #7093137#