megacystis
Image Gallery
[ (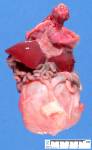 ||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(
||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(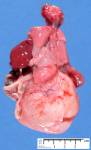 ||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral obstruction})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral obstruction})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with bilateral megaureteres})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis-microcolon syndrome (Case #11183)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis-microcolon syndrome (Case #11183)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis-microcolon syndrome (Case #11183)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral obstruction})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral obstruction})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with bilateral megaureteres})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis with abdominal distension by urethral atresia})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis-microcolon syndrome (Case #11183)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis-microcolon syndrome (Case #11183)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Megacystis-microcolon syndrome (Case #11183)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
[
(||image_reduire{0,60}|inserer_attribut{alt,Prune belly sequence by urethral obstruction sequence with megacystis (Case (...)})
]
Etioogy
![]() fetal urethral obstruction (obstructive megacystis)
fetal urethral obstruction (obstructive megacystis)
- meconium in the urinary bladder (congenital rectovesical fistula)
- urethral atresia (agenesis of the posterior urethra) with or without anorectal agenesis
- posterior urethral valve
![]() non-obstructive megacystis
non-obstructive megacystis
- intestinal neuronal dysplasia
- vesical myopathy (visceral myopathy)
- megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome (MMIHS)
- trisomy 18
- megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome (MMIHS)
![]() chromosomal anomalies
chromosomal anomalies
- trisomy 13
- trisomy 18
- trisomy 21
Mouse models
![]() mgb mouse: transgenic mutant mouse model with in utero megabladder, hydroureteronephrosis, chronic renal failure secondary to obstructive uropathy (primary defect in bladder smooth muscle development) (#17202422#)
mgb mouse: transgenic mutant mouse model with in utero megabladder, hydroureteronephrosis, chronic renal failure secondary to obstructive uropathy (primary defect in bladder smooth muscle development) (#17202422#)
See also
![]() Prune-Belly sequence
Prune-Belly sequence
Case records
![]() Case record #10087
Case record #10087
![]() Case record #11183: megacystis-microcolon syndrome
Case record #11183: megacystis-microcolon syndrome
![]() Case record #11598: Megacystis in urethral obstruction sequence (UOS) with prune belly syndrome
Case record #11598: Megacystis in urethral obstruction sequence (UOS) with prune belly syndrome
References
![]() McHugo J, Whittle M. Enlarged fetal bladders: aetiology, management and outcome. Prenat Diagn. 2001 Nov;21(11):958-63. PMID: #11746149#
McHugo J, Whittle M. Enlarged fetal bladders: aetiology, management and outcome. Prenat Diagn. 2001 Nov;21(11):958-63. PMID: #11746149#