Home > E. Pathology by systems > Digestive system > digestive pneumatosis
digestive pneumatosis
Tuesday 1 July 2003
Digital cases
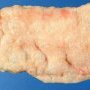
Case 226: Parietal pneumatosis in neonatal necrotic enterocolitis
Definition: Pneumatosis intestinalis is characterized by the accumulation of gas in the gastrointestinal wall.
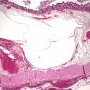
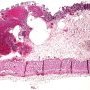
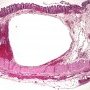
The histopathologic diagnosis is easily made on resection specimens in which the presence of submucosal or subserosal empty spaces lined by histiocytes and giant cells presents little diagnostic dilemma.
In biopsy material, though, the diagnosis is more challenging, as giant cells and histiocytes can be interpreted as granulomatous inflammation indicative of other conditions such as infection or Crohn disease.
Synopsis
pseudo-polyps
raised mucosal folds
submucosal cystic spaces lined by giant cells
giant cells lining a rounded or cleftlike space
pseudolipomatosis
round empty spaces in the submucosa resembling fat
nonspecific findings
- variable inflammation
- eosinophilia
- mild gland disarray
- vascular ectasia
- edema
- mild melanosis coli
Differential diagnosis
granulomatous inflammation
- granulomatous colitis
- Crohn disease
Etiology
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
ischemic colitis
cytomegalovirus colitis
Localization
intestinal pneumatosis
colonic pneumatosis
Synopsis
cryptitis
crypt abscesses
mucosal chronic inflammation
mucosal granulomas
crypt dilation
partial crypt rupture
intramucosal cysts
clusters of small gas cysts in the lamina propria.
Etiology
neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis (NNEC)
anaerobial bacterial enterocolitis
high intraluminal pressure
- cystic fibrosis (16702447, 9530294)
- chronic digestive obstruction
- adhesional obstruction (16420873)
- motility disorders (12.5%)
- sclerodermy (15981628)
- primary intestinal pseudo-obstruction (16271330)
- acute colonic pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie syndrome) (14650951)
Associations
healthy children (22%)
organ and bone marrow transplant (22%)
decompensated congenital heart disease (12.5%)
gastroschisis (9%)
short bowel syndrome (6%)
most common events immediately preceding
- noninfectious colitis (32%)
- acute enteric infection or toxin (27%)
- bowel ischemia (20%)
- gastrointestinal dysmotility (17%)
- graft versus host disease colitis
See also
Pneumatosis
- hepatic pneumatosis
- cerebral pneumatosis
References
Koreishi A, Lauwers GY, Misdraji J. Pneumatosis intestinalis: a challenging biopsy diagnosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Oct;31(10):1469-75. PMID: 17895747
Pieterse AS, Leong AS, Rowland R. The mucosal changes and pathogenesis of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Hum Pathol. 1985 Jul;16(7):683-8. PMID: 4007844