Home > E. Pathology by systems > Urinary system > Kidneys > kidneys
kidneys
Tuesday 4 May 2004
Kidney. Adj. renal
| WKP |
Definition : The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found on the left and right sides of the body in vertebrates. They are located at the back of the abdominal cavity in the retroperitoneal space. In adults they are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.
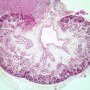
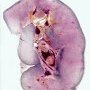
Organ components
cortex
medulla
renal lobules (renal pyramids )
- nephron
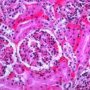
- renal glomeruli (renal glomerulus )
- renal tubules
- proximal convoluted tubule
- descending loop of Henle
- ascending loop of Henle
- distal convoluted tubule
- collecting tubules
- ducts of Bellini
perilobular zones (columns of Bertin )
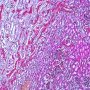
Renal pathology
renal development
renal malformations
renal lesions
renal lesional syndromes
renal diseases
renal tumors
Pathology (Renal pathology )
architectural anomalies
- corticomedullary differentiation anomalies
- lobar organization anomalies
Videos
Histology of the kidneys
@<@object width="425" height="350">@<@param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/9Nh6RBK42qM">@<@/param>@<@param name="wmode" value="transparent">@<@/param>@<@embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/9Nh6RBK42qM" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" wmode="transparent" width="425" height="350">@<@/embed>@<@/object>
Links
Renal Pathology Tutorial by J. Charles Jennette, MD at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Renal Pathology tutorial at University of Washington, Seattle
Renal tumors on wepathology.com (Urology)
ECSYSVASTRIAL
Atlas of renal pathology from American Journal of Kidney Diseases
See also