Home > E. Pathology by systems > Digestive system > Liver and pancreatobiliary system > Liver > ductopenia
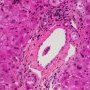
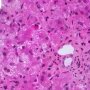
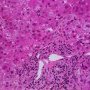
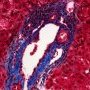
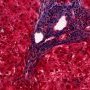
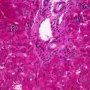
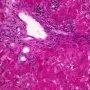
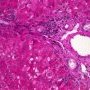
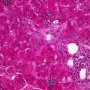
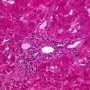
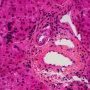
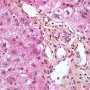
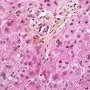
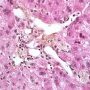
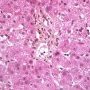
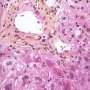
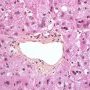
ductopenia
Wednesday 4 June 2003
Etiology
I. Associated forms of bile duct paucity
metabolic and genetic disorders
- alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
- inborn errors of bile acid metabolism
- peroxisomal diseases (cerebrohepatorenal syndrome, Zellweger syndrome)
- coprostanic acidemia
genetic diseases
- chromosomal diseases: 45X (Turner syndrome), trisomy 17, trisomy 18, trisomy 21
- Ellis-van Creveld syndrome (12100513)
- Byler disease
- cystic fibrosis
inflammatory and dysimmune disorders
- auto-immune sclerosing cholangitis
- hepatic GVHD
- chronic hepatic allograft rejection
- hepatic sarcoidosis
bilairy atresia (late)
Hodgkin lymphoma (11241447)
histiocytic hepatic infiltration and histiocytic portal infiltration
- familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (15906086)
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis
panhypopituitarism
drug-induced vanishing bile-duct syndrome
- antibiotic-associated vanishing bile-duct syndrome
fetal infections
- fetal rubella (rubella fetopathy)
- fetal CMV infection (CMV fetopathy)
- fetal syphilis
miscellaneous
- prune belly sequence
- congenital pancreatic hypoplasia associated with paucity of bile ducts and renal microcysts (15214468)
- leprechaunism (9339119)
- PFIC (progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis)
drug-induced ductopenia (drug-induced vanishing bile duct syndrome)
- zonisamide (#17122520 #)
II. idiopathic forms
A. syndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts (Alagille’s syndrome)
B. nonsyndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts
- familial idiopathic childhood ductopenia
- familial idiopathic adulthood ductopenia
References
Desmet VJ, van Eyken P, Roskams T. Histopathology of vanishing bile duct diseases. Adv Clin Path. 1998 Apr;2(2):87-99. PMID: 10358336