Home > F. Pathology by regions > Abdomen > abdominal mesothelial cyst
abdominal mesothelial cyst
Friday 13 January 2006
mesothelial inclusion cysts, benign cystic mesothelioma
The lesions are unifocal and multifocal.
The lesions are located on the surface of the peritoneum in the cul de sac, on the intestines, urinary bladder, uterine adnexa, also involved round ligament within the pelvis and in the inguinal canal.
Additionally, small cysts, free-floating in the peritoneal cavity can be present.
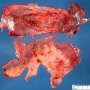
Gross appearance
The lesions can be polycystic.
The surgical materials range from three fragments measuring 0.5 cm each to seven fragments, with the maximum size of 14x6 cm.
The cysts are from microscopic size to 2 cm in diameter.
The majority are thin-walled, semitranslucent, filled with clear or yellowish fluid or gelatinous contents.
In some cases, the cyst walls are thicker and show intense inflammatory lesions and fibrinous exudate.
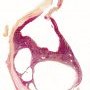
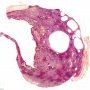
Microscopy
The majority of cysts are lined with a single layer of flattened or cuboid mesothelial cells (CK+, calretinin+).
In some patients, the mesothelium demonstrated diffuse squamous cell metaplasia.
Sometimes, the cells focally form small papillae and are vacuolated.
No mucus is observed either in the cytoplasm or outside the cells.
Immunochemistry
Immunohistochemical reactions to CEA, ER, PR and MIB-1 are negative.
Intramural proliferations and intracystic detached clumps of cells showed both mesothelial cells (without any mitotic activity and signs of atypia) and macrophages (CD68+).
Types
unifocal
multifocal
Localization
diaphragmatic mesothelial cysts
peritoneal surface (surface of the peritoneum)
- peritoneal cul-de-sac
- intestines
- urinary bladder
- uterine adnexa
- round ligament within the pelvis
- inguinal canal
- free-floating cysts in the peritoneal cavity
visceral
- intra-hepatic mesothelial cysts (12489001)
- splenic mesothelial cysts
Synopsis
Gross appearance: polycystic lesions
Size: microscopic size to 2 cm in diameter
thin-walled, semitranslucent, filled with clear or yellowish fluid or gelatinous contents
cysts were with a single layer of flattened or cuboid mesothelial cells (CK+, calretinin+)
diffuse squamous cell metaplasia
cells focally forming small papillae
vacuolated cells
no mucus
Immunohistochemistry
CK +
calretinin +
Associations
diaphragmatic defect (diaphragmatic hernia)
References
Mesothelial inclusion cysts (so-called benign cystic mesothelioma)—a clinicopathological analysis of six cases. Urbańczyk K, Skotniczny K, Kuciński J, Friediger J. Pol J Pathol. 2005;56(2):81-7. PMID: 16092670
Arber DA, Strickler JG, Weiss LM. Splenic mesothelial cysts mimicking lymphagiomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997 Mar;21(3):334-8. PMID: 9060604