Home > E. Pathology by systems > Respiratory system > Lungs > alveolar proteinosis
alveolar proteinosis
Monday 7 March 2005
Digital cases
Case 87 (HPC:87)
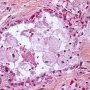
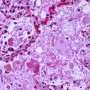
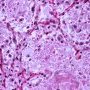
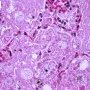
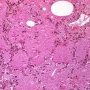
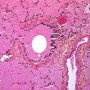
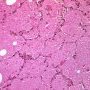
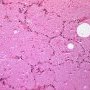
Definition: Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare cause of chronic interstitial lung disease in children characterised by accumulation of a lipoproteinaceous material in the alveoli.
Acquired pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a syndrome characterized by pulmonary surfactant accumulation occurring in association with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor autoantibodies (autoimmune PAP) or as a consequence of another disease (secondary PAP).
Synopsis
Bronchoalveolar lavage
- milky appearance of the return fluid
- periodic acid-Schiff staining material in the alveolar macrophages
- homogeneous, granular material typical of PAP.
Ultrastructure
The material is composed of extracellular, multilamellated bodies when viewed by electron microscopy.
Etiology
genetic primary PAP
- SFTPB mutations with SP-B deficiency (early-onset PAP) (8163685)
- SFTPC mutations with SP-C deficiency (MIM.178620) at 8p21
- ABCA3 mutations with neonatal surfactant deficiency
- CSF2RB mutations (GM-CSF receptor ß subunit) (MIM.138981)
- TTF1 (TITF-1) gene mutation (MIM.600635) (15517377)
- CSF2RB mutations (GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptor common beta chain) (9694696)
acquired pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP)
- adult idiopathic PAP
- autoimmune alveolar proteinosis (autoimmune PAP) (18202348)
secondary PAP (associated PAP)
- immunodeficiency
- constitutional immunodeficiency
- acquired immunodeficiency
- AIDS and HIV infection
- bone marrow allograft (16162733)
- umbilical cord blood transplantation (12111790, 12562244)
- lung allograft recipients (9416695)
- immunosuppression
- corticosteroids
- antirheumatoid arthritis drug leflunomide (16916345)
- leukemias and blood diseases (7429503)
- chronic myeloid leukemia (chronic myelogenous leukemia or CML) (#9568140 #)
- acute myeloid leukemia (16173954, 16432866)
- acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- sideroblastic anemia
- myelodysplastic syndrome (10407875, 12547151)
- Fanconi anemia (Fanconi disease) (515542)
- myelofibrosis after essential thrombocythemia (12854908)
- pulmonary infections
- Pneumocystis carinii
- Nocardia asteroides
- Histoplasma sp.
- systemic infections
- lysinuric protein intolerance (8163273)
- dermatomyositis
- Imatinib treatment (14656624)
- dusts
- NO2 exposure (?) (1870017)
Associations
busulfan lung (2316373)
end-stage pulmonary fibrosis
malignant mesothelioma (15838000)
disseminated atypical mycobacteriosis (2316373)
- disseminated Mycobacterium kansasii infection (14587059)
cytomegalovirus infection (218518)
human parainfluenza virus giant cell pneumonia (12562244)
sporadic associations
- renal tubular acidosis (7742818)
- Fanconi disease (7742818)
- glioblastoma multiforme (7742818)
- atrioventricular septal defect (7742818)
Animal model
development of PAP in
- GM-CSF knock-out mice / (GM-CSF)(-/-) mice
- GM-CSF receptor knock-out mice
References
de Blic J. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004 Dec;5(4):316-22. PMID: 15531257
Trapnell BC, Whitsett JA, Nakata K. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2003 Dec 25;349(26):2527-39. PMID: 14695413
Yousem SA. Alveolar lipoproteinosis in lung allograft recipients. Hum Pathol. 1997 Dec;28(12):1383-6. PMID: 9416695
Bedrossian CW, Luna MA, Conklin RH, Miller WC. Alveolar proteinosis as a consequence of immunosuppression. A hypothesis based on clinical and pathologic observations. Hum Pathol. 1980 Sep;11(5 Suppl):527-35. PMID: 7429503