Home > E. Pathology by systems > Digestive system > Esophagus > eosinophilic esophagitis
eosinophilic esophagitis
Monday 18 October 2004
eosinophilic oesophagitis, allergic esophagitis, allergic eosinophilic esophagitis
Images
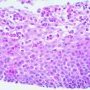
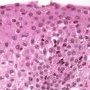
Eosinophilic esophagitis
- https://twitter.com/Konzult_/status/733480083944574976
- https://twitter.com/amy_treece13/status/871513422499790848
- https://twitter.com/Konzult_/status/879515727685922817
- https://twitter.com/smallbluecells/status/879818589636833282
Synopsis
eosoniphils in surface epithelium
- High number of eosinophils (>20/hpf)
- Eosinophil number highest proximally
- Predominance of eosinophils toward luminal surface
- eosinophilic microabscesses
- surface eosinophilic slough
eosinophilic microabscess formation
eosinophilic superficial concentration
high intraepithelial eosinophil counts
intraepithelial mast cells (17204948)
IgE-bearing cells (17204948)
Differential diagnosis
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- peptic esophagitis
See also
eosinophilic infiltrations
eosinophilic digestive diseases
eosinophilic gastroenteropathies
esophagitis
eosinophilic enteropathies
- eosinophilic enteritis
- eosinophilic gastritis
References
Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, Gupta SK, Justinich C, Putnam PE, Bonis P, Hassall E, Straumann A, Rothenberg ME; First International Gastrointestinal Eosinophil Research Symposium (FIGERS) Subcommittees. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007 Oct;133(4):1342-63. Epub 2007 Aug 8. PMID: 17919504
Antonioli DA, Furuta GT. Allergic eosinophilic esophagitis: a primer for pathologists. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2005 Nov;22(4):266-72. PMID: 16939054
Kirsch R, Bokhary R, Marcon MA, Cutz E. Activated mucosal mast cells differentiate eosinophilic (allergic) esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007 Jan;44(1):20-6. PMID: 17204948