Home > E. Pathology by systems > Reproductive system > Female genital system > Breast > mammary invasive lobular carcinoma
mammary invasive lobular carcinoma
Wednesday 9 February 2011
breast invasive lobular carcinoma; invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; mammary infiltrating lobular carcinoma; lobular carcinoma of the breast: mammary invasive lobular carcinoma; infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast
| PO | WPA |
Definition: Invasive lobular carcinoma shows single file infiltrative neoplastic cells, which are negative for E-cadherin and shows cytoplasmic p120 cadherin as opposed to surface p120.
The lesion usually presents as a palpable mass, and mammography tends to underestimate the size of the lesion since it does not have as many calcifications.
Invasive lobular carcinoma has monotonous round malignant cells, frequently infiltrating in single file lines, which are negative for E-cadherin. It is more frequently multifocal than invasive ductal carcinoma.
See also
mammary lobular carcinomas
Links
http://www.webpathology.com/atlas_map.asp?section=9
Images
Invasive and non-invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast
Synopsis
Invasive lobular carcinoma has monotonous round malignant cells, frequently infiltrating in single file lines, which are negative for E-cadherin. It is more frequently multifocal than invasive ductal carcinoma.
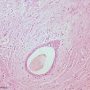
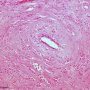
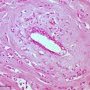
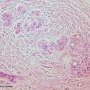
Small uniform tumor cells are seen infiltrating the stroma singly, in a single file (Indian file) pattern or in a concentric fashion around an uninvolved duct.
high power views show relatively uniform vesicular nuclei with small punctate nucleoli. There is abundant dense fibrous stroma.
Classis or pure invasive lobular carcinoma shows absence of solid, alveolar, papillary, or gland-forming units.
The tumor cells are arranged in slender linear strands one to two cells across.
In some foci, the so-called Indian filing is not conspicuous and the tumor cells may just be dispersed in an irregular fashion in the stroma.
In some cases of infiltrating lobular carcinoma, the foci of tumor cells may be inconspicuous and may be easily overlooked at low power.
The tumor cells can infiltrate into the adjacent fat and create an appearance mimicking fat necrosis.
Many cases of infiltrating lobular carcinoma have conspicuous intracytoplasmic lumina in the tumor cells. With mucicarmine and alcian blue stain, mucin can be demonstrated in these lumina.
DECEPTIVE PATTERNS of INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
by Melinda F. Lerwill, M.D.
Look for Invasion When You See:
irregular glandular contours
variation from background architecture
chronic inflammation
increased cellularity in stroma
reactive stroma
Be Especially Attuned to the Possibility of Early Invasion in:
high-grade DCIS / comedo DCIS
LCIS with comedonecrosis
pleomorphic LCIS
mucocele-like lesions
Variants
Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma.
- This tumor has the growth pattern of a classic invasive lobular carcinoma but displays marked nuclear pleomorphism.
- The tumor cell nuclei in this image are variable in size and shape, have irregular contours, and are quite hyperchromatic.
signet-ring morphology
- There can be a transition from classic infiltrating lobular carcinoma to signet-ring morphology.
- Majority of the so-called signet-ring cell carcinomas of the breast are variants of lobular carcinoma.
Histiocytoid carcinoma of the breast
- It is is a variant of infiltrating lobular carcinoma showing apocrine differentiation.
- The tumor cells infiltrate singly or in small clusters and have abundant granular, foamy cytoplasm and enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei.
- The tumor cells resemble histiocytes – hence the name.
- Histiocytoid carcinoma shows immunoreactivity for GCDFP-15.
- Some studies have suggested an aggressive clinical course for this variant of infiltlrating lobular carcinoma.
Digital cases
JRC:5436 : mammary invasive lobular carcinoma.
JRC:5437 : mammary invasive lobular carcinoma.
JRC:5439 : mammary invasive lobular carcinoma. Giant cc variant
JRC:5440 : mammary invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast by Ed Euthman.
Lobular carcinoma lacks functional E-cadherin expression but shares molecular similarities with low-grade invasive ductal carcinomas.
See also
mammary carcinomas
breast cancer