Home > E. Pathology by systems > Respiratory system > Pleura > pleural empyema
pleural empyema
Wednesday 30 November 2005
| WKP |
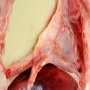
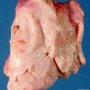
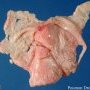
Definition: Pleural empyema (also known as a pyothorax or purulent pleuritis) is an accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity.
Most pleural empyemas arise from a bacterial infection within the lung (pneumonia), often associated with parapneumonic effusions.
There are three stages: exudative, fibrinopurulent and organizing. In the exudative stage, the pus accumulates. This is followed by the fibrinopurulent stage in which there is loculation of the pleural fluid (the creation of pus pockets). In the final organizing stage, scarring of the pleural space may lead to lung entrapment.
See also
Empyema
suppurations
pyogenic infections